Introduction to bibliometrics
Introduction to bibliometrics
Scientific journals are evaluated using bibliometric indicators. Although the objectivity of these indicators is sometimes considered questionable, they are currently regarded as a measure of quality in the academic community. In particular, they are based on citation analysis, which measures which articles or journals are cited more than others. Put simply, those that are cited more than others can be considered to be of higher quality than those that are cited less.
Let's take a look at the most commonly used bibliometric indicators.
Impact Factor
also referred to as Journal Impact Factor
This is currently the most significant citation analysis coefficient, which can express the quality of a particular journal. An impacted journal is a journal that is registered in the Journal Citation Reports (JCR)) database, which assigns it a specific impact factor value. Journal Citation Reports is a sister product to the Web of Science database; JCR calculates indicators based on the content of the Web of Science database.
The impact factor expresses the average number of citations of articles published in a given journal over a certain period (usually two years) in other journals listed in Web of Science. A higher impact factor indicates that the journal is more frequently cited and therefore probably more prestigious.
Example
SOCIOLOGICKY ČASOPIS - CZECH SOCIOLOGICAL REVIEW - ISSN 0038-0288
The JIF value for 2024 for this journal is 0.7.
Article Influence Score (AIS)
The Article Influence Score (AIS) is similar to the Impact Factor (IF). AIS expresses the average number of citations per article over the last 5 years. Individual citations are weighted according to several criteria within the Eigenfactor indicator, with citations from prestigious journals being given greater weight and self-citations not being counted, etc. AIS is more resistant to unfair practices ("citation cartels"). Despite these differences, there is a positive correlation between AIS and IF. Since 2017, AIS has been the main metric for evaluating science in the Czech Republic.
You can find the specific AIS value for a given journal in the Journal Citation Reports.
Example
SOCIOLOGICKY ČASOPIS - CZECH SOCIOLOGICAL REVIEW - ISSN 0038-0288
The AIS value for 2024 for this journal is 0.173.
Scimago Journal Rank (SJR)
A less significant indicator for evaluating journals published in the Scopus database. Also used in government evaluations since 2017.
What are quartiles and deciles?
Impacted journals are ranked within their fields according to various metrics (e.g., impact factor, AIS, SJR, CiteScore). Journals within a field are ranked according to the selected metric from highest to lowest. According to the position in the ranking, the following can then be calculated:
The set of journals can be divided into 4 quartiles (Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4) or 10 deciles (D1 to D10) according to the highest to lowest metric number. For example, in the case of quartile by JIF, the journals are ordered by JIF from highest to lowest and the first 25% are in the first quartile, the next 25% in the second quartile, etc. Similarly, the first 10% are placed in the first decile.
The most prestigious journals are in the first quartile (Q1) and the first decile (D1). Some journals are ranked in multiple fields, so they may have multiple quartile and decile values.

How to find out the IF and quartile of a particular journal?
These metrics are tracked in multiple sources, but the primary one is Journal Citation Reports, or you can use Web of Science, which only provides basic data.
How to find data in Journal Citation Reports
1/ Search the Journal Citation Reports database for a specific journal, ideally by ISSN.
2/ In the Journal Impact Factor field, you can see the current JIF value and the JIF trend over the last years.
(similarly, these metrics can also be searched in the Web of Science database - by clicking on the journal name)
Ex. SOCIOLOGICAL JOURNAL - CZECH SOCIOLOGICAL REVIEW - ISSN 0038-0288
According to JIF for 2022, the journal is ranked 140th out of 149 ranked journals within the field of Sociology. It is therefore included in:
4. Quartile / Q4,
10. decile / D10 (the value must be calculated manually),
percentile - 6,4.
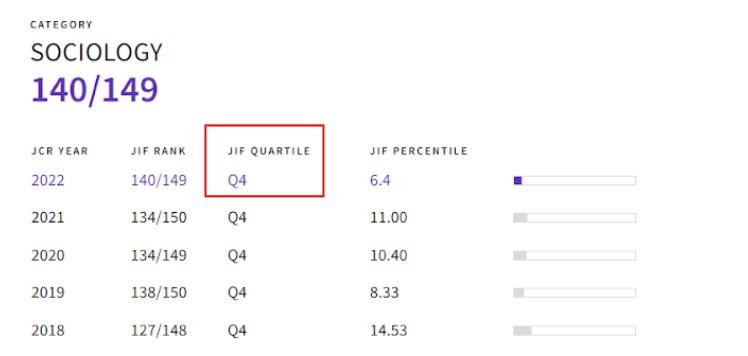
Image: Example of the display of the classification of the journal Sociological Journal according to JIF in the field of Sociology
How do I find impacted journals in my field of study?
1/ In the Journal Citation Reports database, select "Categories".
2/ "Categories" are grouped into large groups, e.g. the group "Social Sciences, General" includes 41 categories in the social sciences - the right arrow will take you to a listing of the categories in that group. Choose the category that best fits the topic of the paper or your field of study and click on it to see a list of journals classified in that category.
Individual categories can appear in multiple indexes of the Web of Science database (SSCI - Social Sciences Citation Index, ESCI - Emerging Sources Citation Index) (note this should change from 2024) and journals can be included in multiple categories at the same time.
3/ The list of journals within a category can be sorted e.g. by number of citations, JIF level, quartile, or a filter tab appears on the left, which offers additional options for working with the list, e.g. to set up multiple categories displayed simultaneously, to limit the search to certain quartiles or JIF ranges, etc.
4/ The final edited list of journals can then be downloaded from the top right via the "Export" button.
H-index
H-index je nástrojem scientometrie. Jde o číselný údaj vypovídající o dopadu práce určitého vědce na oblast jeho činnosti. Číslo h je počtem prací vědce s počtem citací vyšších nebo rovných h. Je hodnocena celková doba vědecké činnosti.
H-index je udáván číslem h, které je množstvím prací, jež byly nejméně h krát citovány. Celkový počet prací je N. Tudíž (N – h) prací má na kontě méně než h citací. Vědec s indexem 50 vydal 50 prací, z nichž každá byla nejméně 50 krát citována (Citací bude tedy nejméně 502=2500).
H-index předpokládá, že dobrý vědec dostatečně publikuje a je dostatečně citován. Předpokládá rovněž, že práce, která je mnohokrát citována, je kvalitní – zde se Hirsch vymezil vůči impakt faktoru (vypovídá o tom, kolikrát byly články daného časopisu citovány – většinou v průběhu roku), který nezohledňuje kvalitu jednotlivých článků každého zvlášť a tím pádem ani schopnosti jejich autorů.
Watch out for that.
It is always important to realise that these indicators are more or less automatically derived and that they are very difficult to compare between disciplines, as different disciplines traditionally have different publishing practices. Thus, a certain Impact factor in medicine will effectively have a different value than in the social sciences. The social sciences traditionally tend to target their best results in books, whereas medical doctors have long targeted their best results in journal articles.

